When children are growing, their facial growth involves increased lower jaw size causing some adjustment to the previous crowded teeth. A 12 year old kid should only have permanent teeth as all their baby teeth had fallen out. A 15 year old child should consult a dentist if he/she still has baby tooth.
Everyone has two sets of teeth
Recently I went on air and I found out that a lot of parents confused over the matter of children’s tooth emergence period. That is why today we are going to talk about this topic and hopefully it could clear some parents’ doubt.
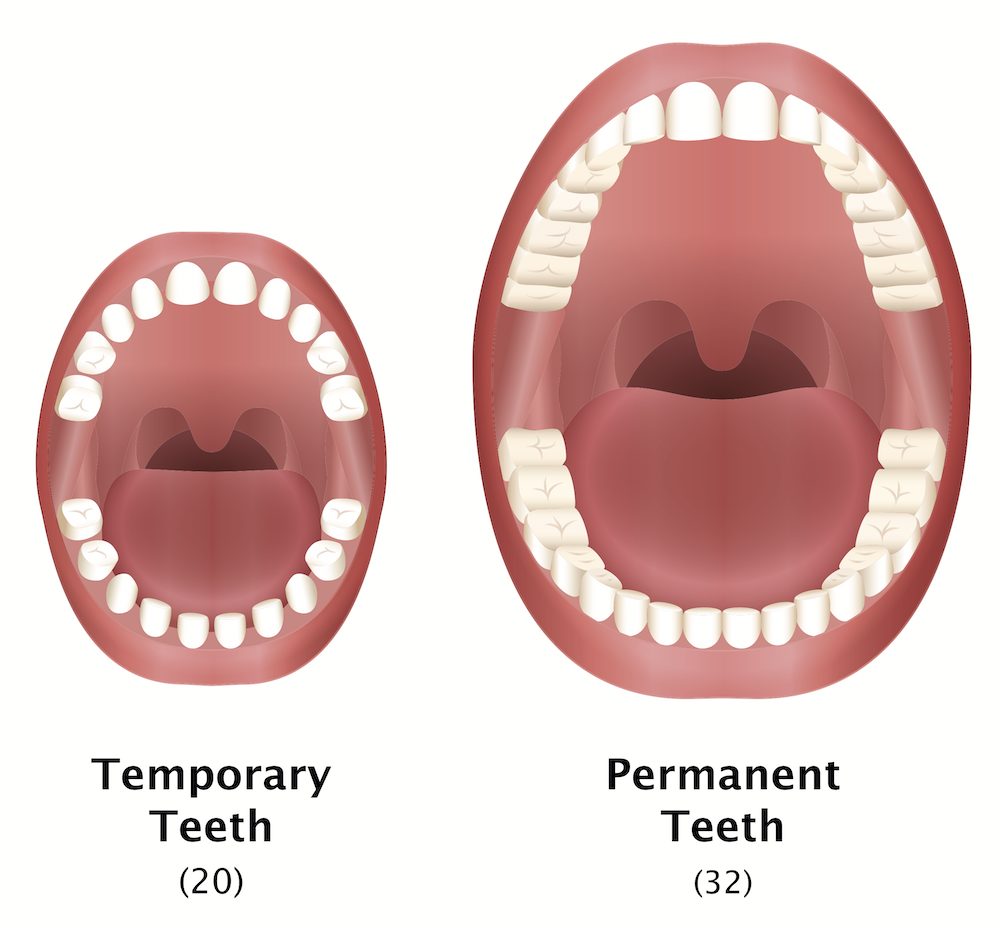
We, humans normally have two sets of teeth, which are baby teeth and permanent teeth. Baby teeth consist of 20 teeth while permanent teeth consist of 32 teeth. You will be wondering why do I say the word “normally”? It is because some children may only have one set of teeth or lesser due to genetic abnormality. So if the baby teeth are being extracted without proper investigation it would render the child toothless for life. Of course, some of the children may have certain missing permanent teeth but still have other teeth that dentition is still in good condition. Therefore, do not easily succumb to extraction of baby teeth and believe that there will be permanent tooth to replace the extracted tooth. Even though only a small part of people encounter this problem but your child might be one of them. X-ray is the best way to let you know whether your child has permanent teeth.
Mal-alignment of teeth would auto adjust
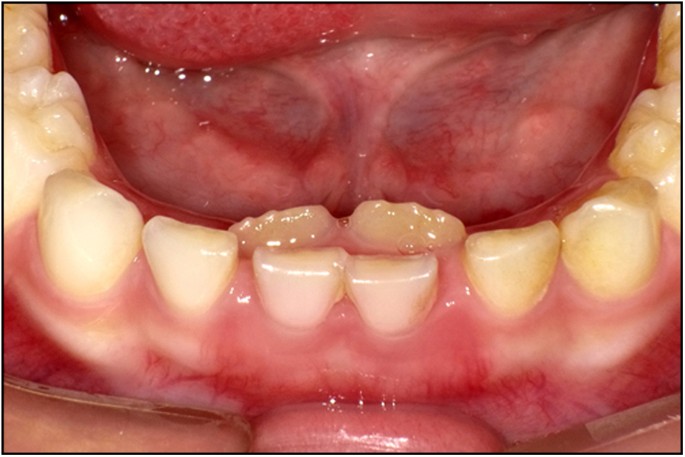
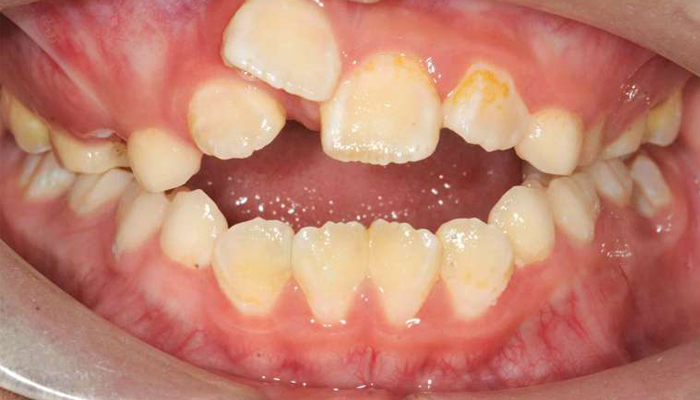
Everyone has to go through 3 stages of teeth development. Baby teeth will emerge and complete from the age of 6 months to 6 years old, giving the child a grand total of 20 baby teeth. This is known as the deciduous stage. At this stage the tooth is orderly arranged on the gums. These teeth are shed between the ages of 6 to 13 years old forming a mixed dentition stage. Usually the permanent teeth are located just below their milk predecessors. With pressure from the permanent tooth, the root of the milk tooth gets dissolved / eaten away, and the milk tooth falls out to make way for the permanent tooth. However, if the permanent tooth is placed too far away, it will erupt even without the primary tooth falling out. This causes double teeth, a new tooth behind or by the side of old one. When a child’s facial bone starts to grow bigger and wider, the size of the jaw increases causing some adjustment to the previous crowded teeth. If it cannot adjust by itself, it’s called malocclusion. To ensure greatest result, it is best to have treatment at the age of 13 to 16.
The differences between baby teeth and permanent teeth
Human’s teeth consist of incisor, canine and molar. Adult’s posterior teeth are classified into premolars and molars. A set of baby teeth include 8 incisors (4 central incisors and 4 lateral incisors), 4 canines and 8 molars, giving a total of 20 baby teeth. On the other hand, a set of permanent teeth include 8 incisors (4 central incisors and 4 lateral incisors), 4 canines, 8 premolars and 12 molars, giving a total of 32 permanent teeth.
Causes of late teething
Babies’ teeth usually emerge at the age of 6 months. Parents do not have to worry if their babies have their first tooth at the age of 1 year old as it is still within the normal range. However babies with no teeth erupting after 1 year old are defined as “delayed teething”. In this case, parents need to check whether late teething is a result of generalized or localizedillness.
Generalized illness is due tomalnutrition especially the lack of vitamin D causing thyroid problems. Localized illness may include gingival fibrosis and eruption cyst. It is not right to just take in additional nutrition but not knowing the real cause of delayed teething. Delayed teething may be due to congenital missing teeth and it is best to undergo X-ray examination to find out the real cause.
The development of baby tooth, permanent tooth and tooth buds
Tooth development does not begin at the stage when babies’ teeth are emerged at the age of 6 months. Tooth development is a long and complicated process. Baby teeth start to form during the embryo phase of 2 months pregnancy and the root formation will be completed at the age of 3 while permanent teeth start to form when the fetus is 4 to 5 months and the root formation will only be completed at the age of 20. For example, deciduous canine will be fully formed within 2 years but permanent canine willonly be fully formed within 10 years.
The tooth bud itself is a group of cells at the end of the dental lamina.Along with the formation of the dental lamina, 10 round epithelial structures, each referred to as a bud, develop at the distal aspect of the dental lamina of each arch. These correspond to the 10 baby teeth of each dental arch, and they signify the bud stage of tooth development.
Tooth budsstart to form when the fetus is around 6 weeks old, amounting 20 tooth buds in total. Permanent tooth buds are formed beneath the deciduous tooth buds replacing the erupted deciduous teeth later. As for permanent molars’ tooth buds, they will form at the age of 10 months in fetal stage, 2 years and 5 years when the baby is born. By then, tooth budding stage completes.
Malformation could happen during stages of root formation
The formation and eruption of tooth and tooth bud are a continuous process. From the eruption of the edge of tooth into the oral cavity until it meets the opposing tooth, malocclusion could occur. External forces could disrupt the normal positioning of a tooth as the tooth’s root formation is incomplete, gums are still loosely attached to the tooth and jaw bones are less compact. The habits of thumb sucking and lip biting can cause malocclusion. If malocclusion persists, it is best for children to have bracesat a young age in order to achieve the best results.
Teething ends at the age of 12
When a child continues to grow the size and number of deciduous teeth could not adapt to the increase in forces of mastication and jaw size. Thus deciduous teeth would start to shed physiologically at the age of 6 until 12 years old. Teething has two stages which consist of shedding of deciduous and emerging of permanents. It takes 6 years for all deciduous teeth to be replaced. Thus after 12 years old, a child should have shed all deciduous teeth. If deciduous teeth are still present when the child reaches 15 years old it is best to go for a dental check up.